Make an Emergency/Makeshift Water Filter

On a Season 5 episode of the popular, post-apocalyptic television show “The Walking Dead” a group of survivors find themselves out of clean water in an unfamiliar area. The character Rosita makes a DIY water filter by cutting off the bottom of an empty plastic bottle and filling it with sand and rocks. She then begins to slowly pour cloudy water from a nearby stream through it. The episode didn’t show the necessary step of sterilizing the water after filtering (whether through boiling, disinfection with a chemical agent such as bleach, or UV exposure to sunlight).
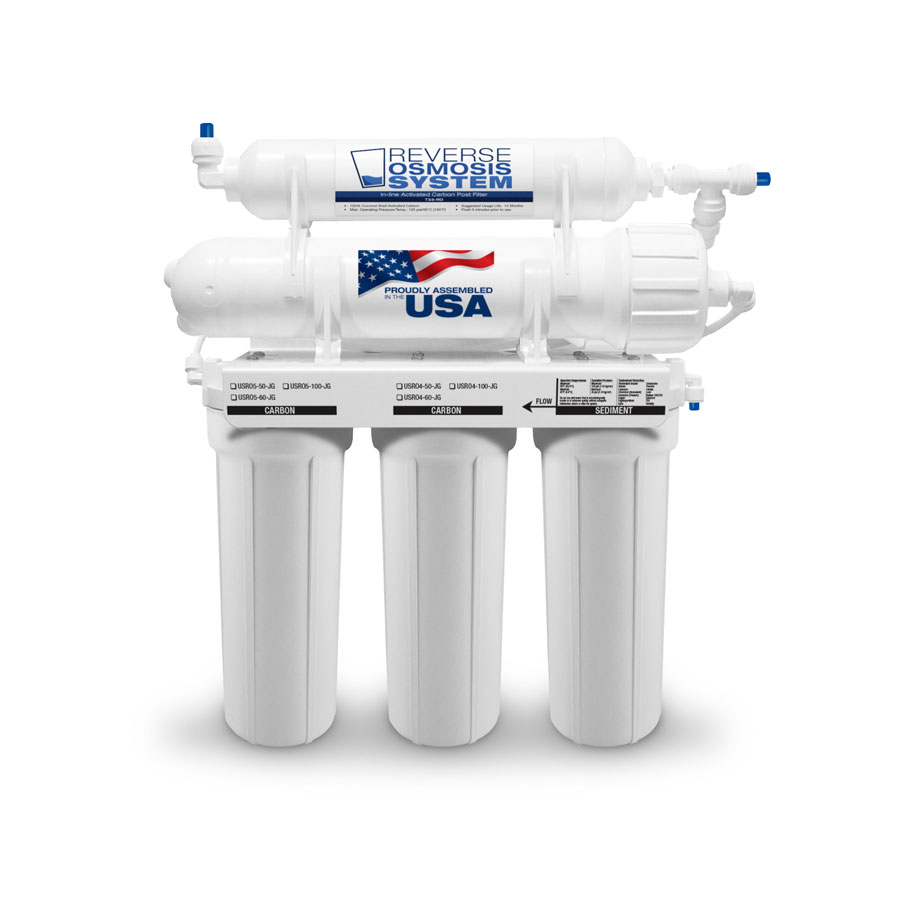
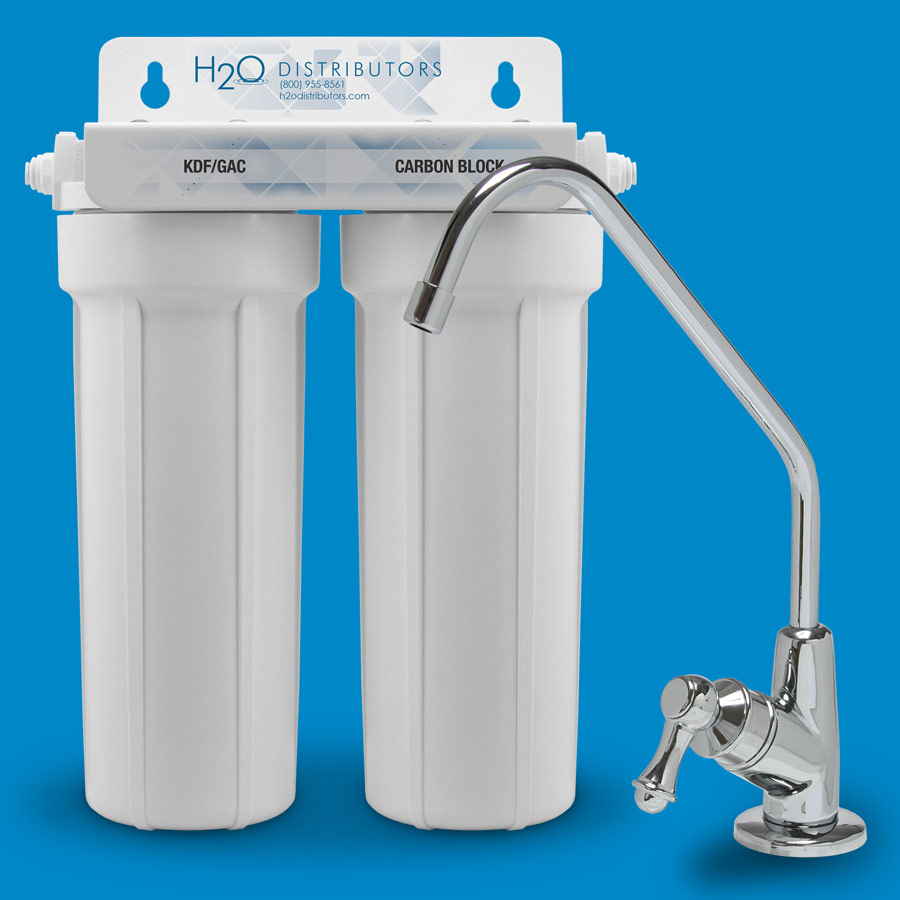
This DIY water filter method does work and can keep you heathly if clean potable water or a manufactured water filter system are unobtainable. It is important to try and find the cleanest water available, and under no circumstances should you try and filter sewage runoff or irradiated water using this process. In a non-emergency situation, a reverse osmosis system, under sink system, countertop or gravity filter would be the way you would want to filter your drinking water.
Materials Needed
- Plastic bottle or comparable food-safe container
- Another container for clean water
- Clean cotton or cheese cloth
- Coffee filter or porous cloth
- Charcoal
- Sand (fine and coarse)
- Gravel or pebbles

Step 1 – Cut Bottom Off
Use scissors or a knife to cut off the bottom part of the bottle you will be putting the filter material in.

Step 2 – Cut Drain Hole
Use scissors or a knife to poke a small hole in the cap. If there is no cap, cut off top of the bottle instead of the bottom for previous step then poke several small holes in the bottom of the bottle.

Step 3 – 1st Layer: Straining Fabric
Stuff the bottom of bottle with a fine cloth or paper fabric, such as a coffee filter, cheese cloth or cotton stuffing.
Sand and grass can also be used in this first stage. Fill the bottom with about 3 inches of grass clippings to filter out larger particulates and help give water a clean taste from chlorophyll contained in the grass. Then fill with 3-4 inches of very fine sand.
Be careful not to use poisonous or unidentified weeds when collect grass clippings. Do not use Highway Department sand, as it can be full of road salt and chemicals.

Step 4 – Break Up Charcoal
Take charcoal from campfire or BBQ charcoal (do not use match/instant light type because it’s soaked in chemicals) and use hammer or rock to break it down into smallest particles you can.

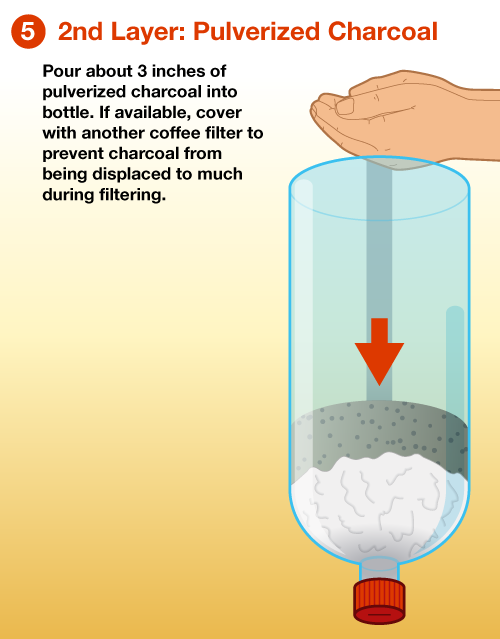
Step 5 – Layer 2: Pulverized Charcoal
Pour about 3 inches of pulverized charcoal into bottle. If available, cover with another coffee filter to prevent charcoal from being displaced to much during filtering.
Step 6 – 3rd Layer: Fine Sand
Add a 2-3 inch layer of the finest sand you can find. This and the subsequent layers you will add are to filter out particulates in the water.
Do not use Highway Department sand, as it can be full of road salt and chemicals.

Step 7 – 4th Layer: Coarse Sand
Add a 2-3 inch layer of coarse sand or very small small pebbles.

Step 8 – 5th Layer: Fine Sand
Add an additional 2-3 inch layer of the fine sand. Multiple varying filter stages (like a reverse osmosis system) ensures that most of the particles present in the water are caught.

Step 9 – 6th Layer: Gravel
Add a 2-3 inch layer of gravel or small rocks to prevent the water being poured in from displacing the sand.

Step 10 – Top Strainer
Cover top of filter with a piece of porous cloth, such as a bandana or cheese cloth. This step is optional but helpful in straining any large debris from the water and stop the pouring from displacing the sand inside the filter.

Step 11 – Pouring & Collecting
Pour water slowly into filter while holding it over the second container.
Make sure to wipe off or clean the collection container. Pour water slowly so as not to disturb filter layers too much or to cause filter container to overflow and possibly spilling unfiltered water into collection container.

Step 12 – Sterilize Water
Even though you have filtered the water through many different layers, microbes can still exist in the water and it still needs to be sterilized. Boiling the water in a pot or kettle is the easiest way.
You can also use sunlight to sterilize water. Pour filtered water into a clean, clear plastic or glass bottle up to 3/4 full and screw on cap. Shake for thirty seconds to add more oxygen to the water. Place on light or reflective surface in direct sunlight. The amount of exposure it needs it dependant on weather conditions. A clear day requires 6 hours of exposure whereas 50% or more cloud coverage will require 2 days of sunlight. Here is a DIY water filter!

Why do these layers help?
- Gravel catches larger particles.
- Sand traps small sediment for clearer water.
- Activated carbon reduces chlorine and some organic compounds and improves taste and odor.
Limitations
DIY filters do not reliably reduce microbes, dissolved salts, heavy metals, PFAS, or all chemicals. Use certified systems when water quality is uncertain or when contaminants are known to be present.
Better every day options
For daily drinking water, consider a carbon under-sink system for taste and odor, a reverse osmosis system for dissolved solids, or a whole house carbon system for every tap. Select capacity and cartridges that match your water source and usage requirements.
Q&A on DIY Water Filters
Q: Will a DIY filter remove bacteria and viruses?
A: No. It improves clarity and taste but does not reliably remove microbes. Always boil or use a certified purifier.
Q: Can I use charcoal from a grill instead of activated carbon for a DIY filter?
A: No. Use food-grade activated carbon specifically designed for water treatment. Grill charcoal can contain additives and is not safe for drinking water filtration.
Q: Does boiling replace the need for a filter?
A: Boiling kills microbes but does not remove sediment or chemicals. Filtering first improves clarity, then boiling enhances safety.
Q: What if my water has a chlorine taste?
A: Activated carbon is effective for reducing chlorine and improving taste. An under-sink carbon filter is a reliable everyday solution.
Q: Is sand from outside safe to use for a homemade water filter?
A: Only use clean, rinsed sand sold for aquariums or filtration. Outdoor sand can introduce contaminants.
Q: Can a DIY water filter help with sulfur or rotten egg smell from a well?
A: Activated carbon may help with odor, but persistent sulfur typically needs targeted treatment. Consider a system designed for well water issues.
Browse some of our popular systems:
A Homemade Water Filter Isn’t Working? Shop for Water Filtration Systems, Water Filters, and Parts Now Ready for water you will love to drink every day? Contact H2O Distributors for assistance in selecting the ideal under-sink, RO, or whole house system for your home.